Hello dog lovers, today Atopic Dermatitis In German Shepherds is my topic, here I explain what it is, its causative agents, its signs and symptoms, and at the end its prevention and control.
Atopic dermatitis is a common allergic skin disease that can affect German Shepherds, among other breeds. Here’s a brief overview of atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds:

Hello everyone who loves dogs! I’m Dr. Arif Aziz, and I’ve been taking care of pets especially dogs at my clinic for a long time, exactly 14 years! I’m here to share some valuable information with you that I’ve gathered from books during my study time written by experts in veterinary medicine (DVM) and MSC (Master of Science), as well as from my own experiences working with dogs.
Atopic Dermatitis in German Shepherds: step by step:
Firstly Understand What Atopic Dermatitis Is:
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itching, redness, and skin lesions. It is caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold, and certain foods.
Atopic dermatitis is a persistent inflammatory skin disorder commonly found in both humans and animals, including dogs. This chronic condition displays as redness, itching, and the development of skin lesions, which can significantly impact the affected individual’s quality of life.
The underlying cause of atopic dermatitis lies in an abnormal immune response to environmental allergens. These allergens can vary widely but commonly include substances like pollen, dust mites, molds, and specific food ingredients. When individuals with atopic dermatitis come into contact with these allergens, their immune system reacts excessively, generating inflammation and skin irritation.
Now we understand the 15 causes of Atopic Dermatitis In German Shepherds:
Atopic dermatitis can have various causes, including genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and immune system abnormalities. Here are 15 potential causes:
Genetics:
Atopic dermatitis often has a genetic component, with certain breeds or individuals being more prone to developing the condition.
Immune System Abnormalities:
Dysfunction in the immune system can lead to an exaggerated response to environmental allergens, triggering inflammation and skin irritation.

Environmental Allergens:
Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, and certain foods can provoke allergic reactions and contribute to the development of atopic dermatitis.
Food Allergies:
Some individuals may develop atopic dermatitis as a result of food allergies or sensitivities, particularly to common allergenic ingredients such as grains, dairy, and proteins like chicken or beef.
Contact Allergens:
Contact with irritants or allergens in the environment, including harsh chemicals, soaps, perfumes, and fabrics, can worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms.
Weather Conditions:
Changes in weather, humidity levels, and temperature extremes can influence skin hydration and barrier function, potentially triggering flare-ups of atopic dermatitis.
Skin Barrier Dysfunction:
Individuals with impaired skin barrier function are more susceptible to moisture loss, irritants, and allergens, which can contribute to the development of atopic dermatitis.
Microbial Infections:
Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections of the skin can exacerbate atopic dermatitis symptoms and contribute to inflammation and skin lesions.
Stress and Emotional Factors:
Emotional stress and anxiety can worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms through their effects on immune function and hormonal regulation.
Hormonal Changes:
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menstruation, can influence immune responses and trigger or worsen atopic dermatitis.
Excessive Scratching:
Persistent scratching or rubbing of the skin can damage the skin barrier, increase inflammation, and exacerbate atopic dermatitis symptoms.
Exposure to Tobacco Smoke:
Secondhand smoke and environmental tobacco exposure have been linked to an increased risk of atopic dermatitis in both children and adults.
Airborne Pollutants:
Exposure to air pollutants such as particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and diesel exhaust particles can contribute to skin inflammation and worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms.
Occupational Exposures:
Certain occupations involving frequent exposure to irritants or allergens, such as healthcare workers, hairdressers, and cleaners, may have a higher risk of developing atopic dermatitis.
Medications:
Some medications, including antibiotics, antihistamines, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can potentially trigger or exacerbate atopic dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
Here’s the information presented in a table format with short descriptions:
| Cause | Description |
| Genetics | Inherited predisposition to atopic dermatitis, with certain breeds or individuals being more susceptible. |
| Immune System Abnormalities | Dysregulation of the immune response leads to exaggerated reactions to environmental allergens. |
| Environmental Allergens | Exposure to substances like pollen, dust mites, and mold spores that provoke allergic reactions. |
| Food Allergies | Sensitivities or allergies to specific food ingredients, such as grains, dairy, or proteins. |
| Contact Allergens | Irritants or allergens in the environment, including chemicals, soaps, perfumes, and fabrics. |
| Weather Conditions | Changes in weather, humidity, and temperature affect skin hydration and barrier function. |
| Skin Barrier Dysfunction | Impaired skin barrier function increases susceptibility to moisture loss, irritants, and allergens. |
| Microbial Infections | Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections that exacerbate symptoms and contribute to skin inflammation. |
| Stress and Emotional Factors | Psychological stress and anxiety can worsen symptoms through effects on immune function and hormones. |
| Hormonal Changes | Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during puberty, pregnancy, or menstruation, can influence symptoms. |
| Excessive Scratching | Persistent scratching damages the skin barrier, increases inflammation and worsens symptoms. |
| Exposure to Tobacco Smoke | Secondhand smoke and environmental tobacco exposure increase the risk of developing atopic dermatitis. |
| Airborne Pollutants | Exposure to pollutants like particulate matter and volatile organic compounds can worsen skin inflammation. |
| Occupational Exposures | Certain occupations with frequent exposure to irritants or allergens may increase the risk of atopic dermatitis. |
| Medications | Some medications, including antibiotics and NSAIDs, can potentially trigger or exacerbate symptoms. |
Understanding these potential causes can help in managing and preventing atopic dermatitis in affected individuals.

Here are 15 signs and symptoms commonly associated with atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds:
Excessive itching (pruritus)
Persistent scratching of the skin
Excessive licking or chewing of the skin or paws
Rubbing against furniture or other surfaces to relieve itching
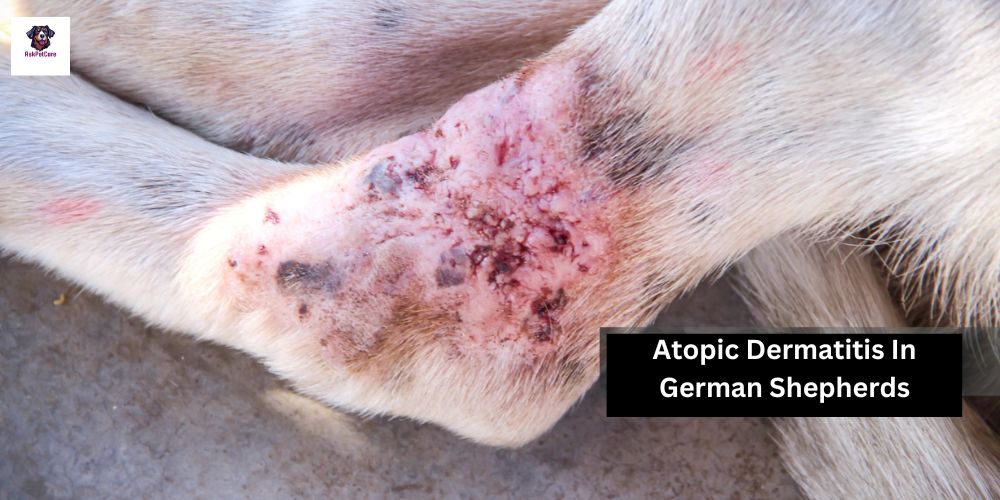
Skin lesions, including redness and inflammation
The presence of papules (small raised bumps) on the skin
Crusted areas on the skin surface
Hair loss or thinning of the coat
Dry, flaky skin
Thickened skin (lichenification) in chronic cases
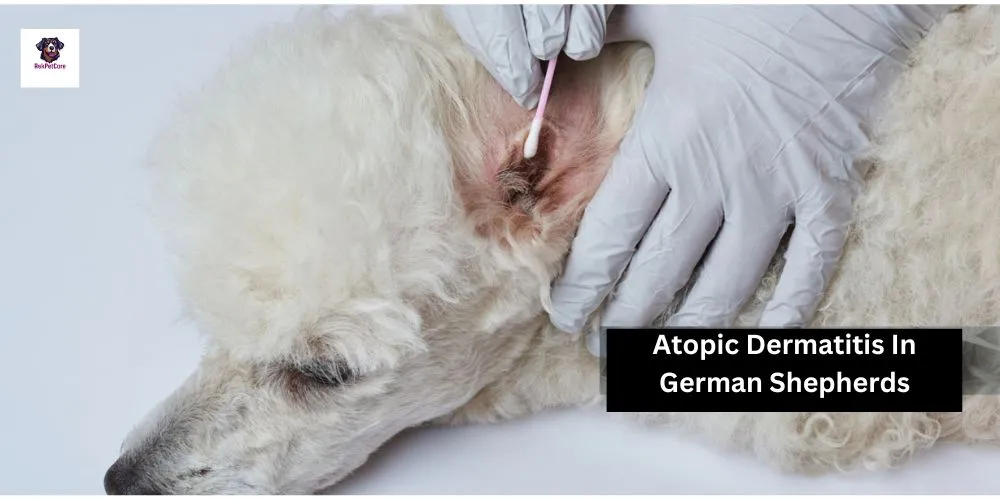
Recurrent ear infections, characterized by redness, odor, and discharge
Moist, irritated areas on the skin (hot spots)
Secondary bacterial or yeast infections due to scratching and broken skin
Discomfort or irritability, especially during flare-ups
Changes in behavior, such as restlessness or agitation due to itching discomfort
These signs and symptoms can vary in severity and may come and go depending on factors such as environmental allergens, stress levels, and the effectiveness of treatment. If you notice any of these signs in your German Shepherd, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and management of atopic dermatitis.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and allergy testing, including intradermal skin testing or blood tests to identify specific allergens.
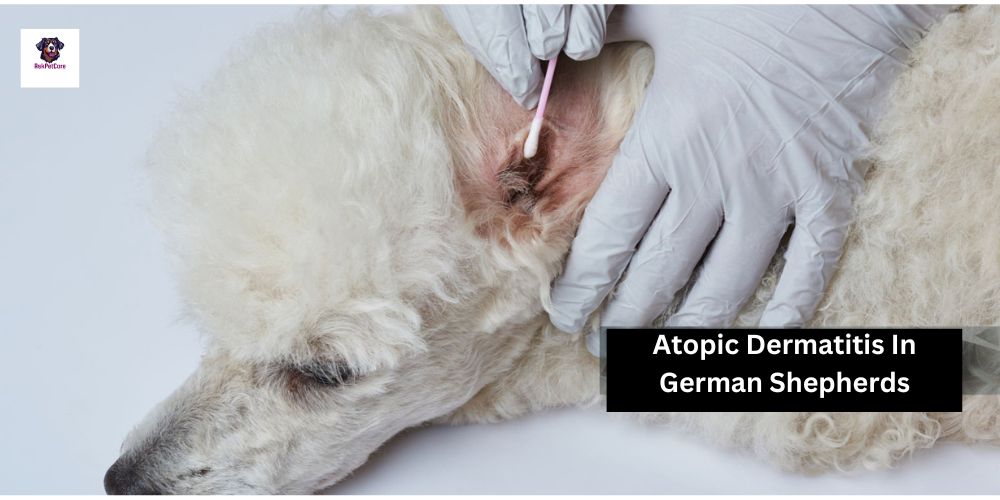
Here are ten methods used in diagnosing atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds:
Medical History: A comprehensive review of the dog’s medical history, including previous skin conditions, allergies, and environmental exposures.
Physical Examination: Thorough examination of the skin, coat, and ears to assess the presence and severity of symptoms such as itching, redness, inflammation, lesions, and ear infections.
Allergy Testing: Intradermal skin testing (skin prick tests) to identify specific allergens that may be triggering the allergic reaction leading to atopic dermatitis.
Blood Tests: Serologic testing, such as serum allergen-specific IgE testing, to detect elevated levels of antibodies associated with specific allergens.
Elimination Diet Trial: Dietary trials involving the exclusion of potential food allergens to determine if food allergies are contributing to the dermatitis.
Skin Biopsy: Collection of skin tissue samples for histopathological examination to assess inflammation, cellular changes, and other histological features characteristic of atopic dermatitis.
Skin Scraping: Microscopic examination of skin scrapings to rule out parasitic infections, such as mange mites, which may mimic symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
Cytology: Microscopic examination of skin swabs or ear discharge to identify bacterial or yeast infections secondary to atopic dermatitis.
Response to Treatment: Evaluation of the dog’s response to symptomatic treatment, such as antipruritic medications or hypoallergenic diets, can help confirm the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis.
Environmental Assessment: Assessment of the dog’s living environment, including exposure to potential allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, and chemicals, to identify and minimize triggers.
These diagnostic methods help veterinarians accurately diagnose atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds and develop targeted treatment plans to manage the condition effectively.
Here’s the information presented in a table format with brief descriptions:
| Diagnosis Method | Description |
| Medical History | Comprehensive review of the dog’s medical background, including past skin conditions and allergies. |
| Physical Examination | Thorough assessment of the skin, coat, and ears to evaluate the presence and severity of symptoms. |
| Allergy Testing | Intradermal skin testing or blood tests to identify specific allergens triggering atopic dermatitis. |
| Blood Tests | Serologic testing to detect elevated levels of antibodies associated with specific allergens. |
| Elimination Diet Trial | Dietary trials to exclude potential food allergens and determine if food allergies are contributing. |
| Skin Biopsy | Collection of skin tissue samples for histopathological examination to assess inflammation and changes. |
| Skin Scraping | Microscopic examination of skin scrapings to rule out parasitic infections such as mange mites. |
| Cytology | Microscopic examination of skin swabs or ear discharge to identify bacterial or yeast infections. |
| Response to Treatment | Assessment of the dog’s response to symptomatic treatment to confirm the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis. |
| Environmental Assessment | Evaluation of the dog’s living environment to identify and minimize exposure to potential allergens. |
These diagnostic methods play a crucial role in accurately diagnosing atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds and formulating effective treatment strategies.
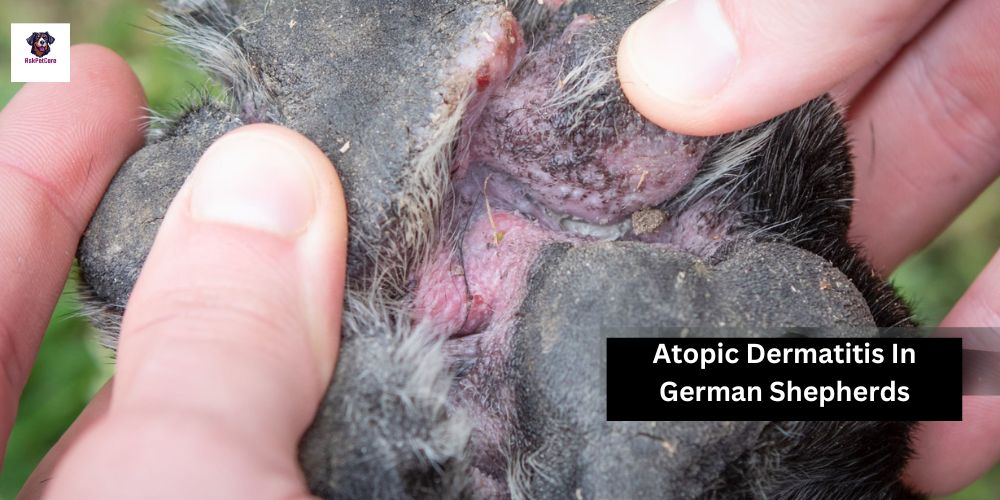
Treatment:
Treatment options for atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds may include allergen avoidance, symptomatic relief with medications such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, and cyclosporine, immunotherapy (allergy shots), and topical therapies to manage skin inflammation and secondary infections.
Here are ten methods used in treating atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds:
Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and minimizing exposure to specific allergens that trigger allergic reactions, such as pollen, dust mites, and certain foods.
Medications:
Antihistamines:
Oral medications help reduce itching and inflammation by blocking histamine receptors.
Corticosteroids:
Topical or systemic steroids that provide anti-inflammatory effects and alleviate itching and redness.
Cyclosporine:
Immunosuppressive medication helps modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation associated with atopic dermatitis.
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots):
Subcutaneous injections of allergens in gradually increasing doses desensitize the immune system and reduce allergic reactions over time.
Topical Therapies:
Topical Steroids: Creams or ointments containing corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching.
Topical Antimicrobials: Products containing antiseptics or antibiotics to treat or prevent secondary bacterial or yeast infections.
Emollients: Moisturizing creams or lotions to soothe and hydrate dry, irritated skin.
Essential Fatty Acid Supplementation: Adding omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid supplements to the dog’s diet to help maintain skin barrier function and reduce inflammation.
Hypoallergenic Diets: Switching to hypoallergenic or novel protein diets to identify and eliminate potential food allergens contributing to atopic dermatitis.
Environmental Controls: Implementing measures to reduce exposure to environmental allergens, such as using air purifiers, hypoallergenic bedding, and frequent cleaning.
Bathing and Grooming: Regular bathing with gentle, hypoallergenic shampoos and conditioners to cleanse the skin, remove allergens, and soothe irritation.
Alternative Therapies: Some owners may explore complementary treatments such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or homeopathy to help manage symptoms and improve skin health.
Lifestyle Modifications: Providing a stress-free environment, maintaining a healthy weight, and promoting regular exercise can support overall health and reduce the severity of atopic dermatitis symptoms.

These treatment options can be tailored to the individual needs of the German Shepherd and may involve a combination of approaches to effectively manage atopic dermatitis and improve the dog’s quality of life. It’s important to work closely with a veterinarian to develop a comprehensive treatment plan and monitor the dog’s response to therapy.
Here’s the information presented in a table format with brief descriptions:
| Treatment Method | Description |
| Allergen Avoidance | Identifying and minimizing exposure to specific allergens triggering allergic reactions. |
| Antihistamines | Oral medications help reduce itching and inflammation by blocking histamine receptors. |
| Corticosteroids | Topical or systemic steroids that provide anti-inflammatory effects and alleviate itching. |
| Cyclosporine | Immunosuppressive medication that helps modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation. |
| Immunotherapy | Subcutaneous injections of allergens to desensitize the immune system and reduce allergic reactions. |
| Topical Steroids | Creams or ointments containing corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching. |
| Topical Antimicrobials | Products containing antiseptics or antibiotics to treat or prevent secondary infections. |
| Emollients | Moisturizing creams or lotions to soothe and hydrate dry, irritated skin. |
| Essential Fatty Acids | Supplements containing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids to maintain skin barrier function. |
| Hypoallergenic Diets | Switching to hypoallergenic or novel protein diets to identify and eliminate food allergens. |
| Environmental Controls | Measures to reduce exposure to environmental allergens, such as using air purifiers and hypoallergenic bedding. |
| Bathing and Grooming | Regular cleansing of the skin with hypoallergenic shampoos and conditioners to remove allergens. |
| Alternative Therapies | Complementary treatments such as acupuncture or herbal remedies to manage symptoms. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Providing a stress-free environment and promoting regular exercise to support overall health. |
These treatment methods can be combined and tailored to the individual needs of the German Shepherd to effectively manage atopic dermatitis and improve quality of life. Always consult with a veterinarian to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
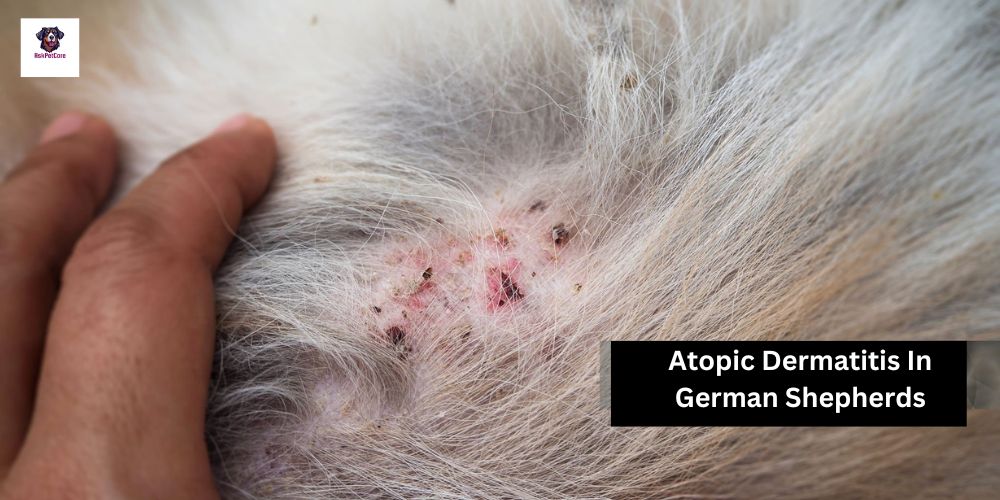
Management:
Managing atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds requires a multifaceted approach that includes identifying and minimizing exposure to allergens, maintaining a healthy diet and weight, regular grooming and bathing with hypoallergenic shampoos, and ongoing veterinary care to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
Here are ten methods used in managing atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds:
Identifying and Minimizing Allergen Exposure: Determine and reduce exposure to common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and certain foods to alleviate symptoms.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Provide a balanced and nutritious diet rich in essential nutrients to support skin health and overall well-being.
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the joints and minimize the risk of obesity-related skin issues.
Regular Grooming and Bathing: Implement a consistent grooming routine, including regular brushing and bathing with hypoallergenic shampoos to remove allergens and soothe the skin.
Skin Miniaturization: Use moisturizers or emollients to hydrate and soothe dry, irritated skin, helping to maintain the skin barrier function.
Environmental Controls: Implement measures such as air purifiers, hypoallergenic bedding, and frequent cleaning to minimize exposure to environmental allergens.
Medication Compliance: Administer prescribed medications as directed by the veterinarian to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Allergy Testing and Immunotherapy: Undergo allergy testing to identify specific allergens and consider immunotherapy (allergy shots) to desensitize the immune system and reduce allergic reactions over time.
Stress Reduction: Minimize stressors and provide a calm, comfortable environment to help alleviate anxiety and reduce the risk of stress-induced flare-ups.
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Schedule routine veterinary visits to monitor the condition, assess treatment efficacy, and make adjustments as needed to optimize management.
By employing these management strategies in conjunction with veterinary guidance, owners can help mitigate the impact of atopic dermatitis on their German Shepherd’s quality of life and promote overall skin health.
Lifestyle Considerations: Owners of German Shepherds with atopic dermatitis should be prepared for long-term management of the condition and work closely with their veterinarian to develop a customized treatment plan tailored to their dog’s specific needs. It’s essential to address the underlying cause of the allergy and provide symptomatic relief to improve the dog’s quality of life and prevent complications.
Here are ten lifestyle considerations for owners of German Shepherds with atopic dermatitis:
Long-Term Management: Understand that atopic dermatitis requires ongoing care and management throughout the dog’s life.
Veterinary Collaboration: Work closely with a veterinarian to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the dog’s specific needs.
Identifying Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to potential allergens, including environmental triggers and food allergens, to reduce flare-ups.
Consistent Medication: Administer prescribed medications consistently and as directed by the veterinarian to effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the dog’s condition, assess treatment efficacy, and make necessary adjustments.
Allergy Testing: Consider allergy testing to identify specific allergens triggering the dog’s atopic dermatitis and guide treatment decisions.
Environmental Modifications: Implement environmental modifications such as using air purifiers, hypoallergenic bedding, and regular cleaning to minimize exposure to allergens.
Dietary Management: Provide a balanced and nutritious diet tailored to the dog’s individual dietary needs, considering potential food allergies or sensitivities.
Skin Care Routine: Establish a consistent skincare routine, including regular grooming, bathing with hypoallergenic shampoos, and moisturizing to maintain skin health.
Stress Reduction: Minimize stressors in the dog’s environment and provide a calm, comfortable atmosphere to help reduce anxiety and prevent stress-induced flare-ups.
By considering these lifestyle factors and working closely with veterinary professionals, owners can help manage their German Shepherd’s atopic dermatitis effectively, improve the dog’s quality of life, and prevent complications associated with the condition.
Overall, while atopic dermatitis can be challenging to manage, with proper care and veterinary guidance, German Shepherds affected by this condition can lead comfortable and fulfilling lives.
What is the scale for atopic dermatitis in dogs?
The scale commonly used to assess the severity of atopic dermatitis in dogs is the Canine Atopic Dermatitis Extent and Severity Index (CADESI). This index evaluates the extent and severity of skin lesions, including erythema (redness), papules (small raised bumps), crusts, excoriations (scratch marks), and lichenification (thickened skin) in various body regions. The CADESI score helps veterinarians monitor the progression of atopic dermatitis and assess the effectiveness of treatment over time.
The Canine Atopic Dermatitis Extent and Severity Index (CADESI) is a tool used by veterinarians to quantify the extent and severity of atopic dermatitis in dogs. Atopic dermatitis is a common allergic skin condition in dogs characterized by itching, redness, and inflammation.
The CADESI evaluates different aspects of the skin lesions associated with atopic dermatitis across various body regions. These aspects include:
Erythema (Redness): This refers to the redness of the skin, which indicates inflammation.
Papules (Small Raised Bumps): Papules are small, raised bumps on the skin that may be red or inflamed.
Crusts: Crusts are dried secretions, such as pus or serum, that form on the surface of the skin.
Excoriations (Scratch Marks): Excoriations are superficial wounds or abrasions caused by scratching or rubbing the skin.
Lichenification (Thickened Skin): Lichenification refers to the thickening and hardening of the skin, often resulting from chronic inflammation and scratching.
The CADESI score is determined by assessing the severity of these skin lesions in different body regions, such as the head and neck, trunk, limbs, and paws. Veterinarians assign a numerical score to each body region based on the severity and extent of the lesions present.
By calculating the CADESI score, veterinarians can objectively measure the severity of atopic dermatitis and track changes in the condition over time. This helps guide treatment decisions and assess the effectiveness of interventions, such as medications, dietary changes, and environmental management strategies.
Overall, the CADESI provides valuable information for both veterinarians and dog owners in managing atopic dermatitis and improving the quality of life for affected dogs.
What are German Shepherds most commonly allergic to?
German Shepherds, like many other breeds, can be allergic to a variety of substances. Some of the most common allergens that German Shepherds may react to include:
- Pollen: Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds can trigger allergic reactions in German Shepherds, leading to symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and skin irritation.
- Dust Mites: These microscopic organisms thrive in indoor environments, especially in bedding, carpets, and upholstery. Dust mite allergies can cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, and discomfort for German Shepherds.
- Fleas: Flea saliva contains proteins that can trigger allergic reactions in dogs, including German Shepherds. Flea allergies often manifest as intense itching, redness, and skin inflammation, particularly around the base of the tail and hindquarters.
- Certain Foods: German Shepherds may develop food allergies or sensitivities to specific ingredients in their diet, such as beef, chicken, wheat, soy, dairy products, and artificial additives. Food allergies can result in digestive issues, skin problems, and allergic reactions.
- Environmental Allergens: Environmental allergens such as mold spores, dander, and certain household chemicals can provoke allergic reactions in German Shepherds, causing symptoms ranging from skin irritation to respiratory distress.
- Certain Medications: Some German Shepherds may be allergic to certain medications or topical treatments, including antibiotics, flea preventatives, and grooming products. Allergic reactions to medications can vary in severity and may require immediate veterinary attention.
Identifying the specific allergens triggering allergic reactions in German Shepherds typically involves a combination of diagnostic tests, including intradermal skin testing, blood tests, and elimination diets. Once the allergens are identified, avoidance strategies, allergen-specific immunotherapy, and symptomatic treatments can help manage allergic reactions and improve the dog’s quality of life. Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of allergies in German Shepherds.
I hope you will understand about atopic dermatitis in German Shepherds, still any query contact me.
Here are some reference books that are considered authoritative on the topic:
These books cover a range of topics related to dermatology and skin diseases in dogs, including diagnosis, treatment, and management of skin conditions.
- “Muller and Kirk’s Small Animal Dermatology” by William H. Miller Jr. DVM DACVD, Craig E. Griffin DVM DACVD, Karen L. Campbell DVM DACVD :
- “Skin Diseases of the Dog and Cat” by Nicole A. Heinrich DVM DACVD, Melissa Eisenschenk DVM DACVD – :
- “Canine and Feline Dermatology Drug Handbook” by Sandra N. Koch DVM MS DACVD, Cheryl S. Hedlund DVM MS DACVD :
Frequently asked questions:
- What causes atopic dermatitis in dogs?
- Atopic dermatitis in dogs is primarily caused by allergic reactions to environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and certain foods.
- What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis in dogs?
- Common symptoms of atopic dermatitis in dogs include itching, redness, skin lesions, hair loss, and recurrent ear infections.
- How is atopic dermatitis diagnosed in dogs?
- Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in dogs typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes allergy testing such as intradermal skin testing or blood tests.
- What breeds are prone to atopic dermatitis in dogs?
- Breeds commonly predisposed to atopic dermatitis in dogs include Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, German Shepherds, and Bulldogs, among others.
- How is atopic dermatitis treated in dogs?
- Treatment options for atopic dermatitis in dogs may include allergen avoidance, medications like antihistamines and corticosteroids, immunotherapy, and topical therapies to manage skin inflammation and infections.
Disclaimer: This information is general advice only. Before starting any treatment or supplement with your pet, please consult your vet first for the best approach to getting your pet back to its best health.
